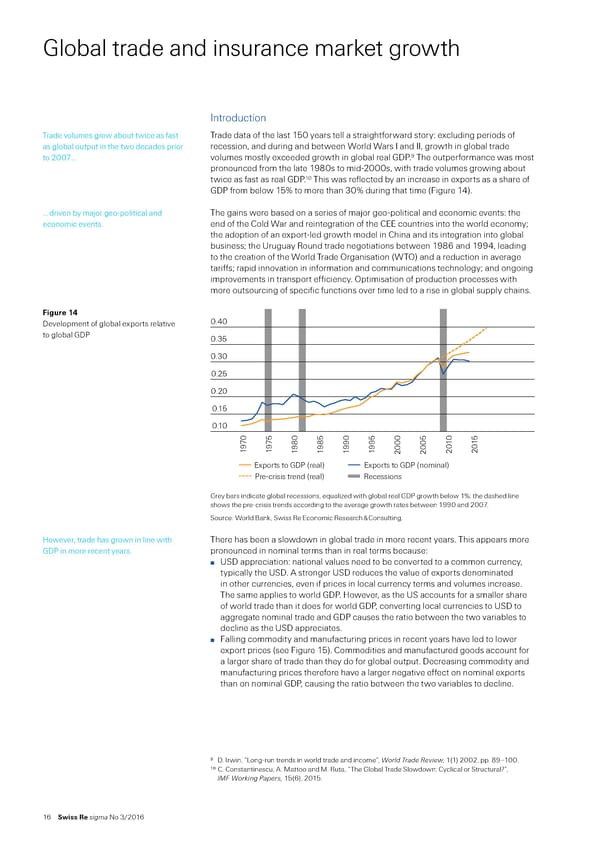
lobal trade and insurance maret growth ntroduction Trade volumes grew about twice as ast Trade data o the last 10 years tell a straightorward story“ excluding periods o as global output in the two decades prior recession‰ and during and between Œorld Œars and ‰ growth in global trade volumes mostly exceeded growth in global real €…¡ to 200ƒ … The outperormance was most pronounced rom the late 1¡0s to midŽ2000s‰ with trade volumes growing about 10 twice as ast as real €… This was relected by an increase in exports as a share o € rom below 1ˆ to more than 30ˆ during that time †¥igure 1’‡… … driven by maŠor geoŽpolitical and The gains were based on a series o maŠor geoŽpolitical and economic events“ the economic events… end o the —old Œar and reintegration o the —EE countries into the world economyŸ the adoption o an exportŽled growth model in —hina and its integration into global businessŸ the ‹ruguay ˜ound trade negotiations between 1¡6 and 1¡¡’‰ leading to the creation o the Œorld Trade ¢rganisation †ŒT¢‡ and a reduction in average tarisŸ rapid innovation in inormation and communications technologyŸ and ongoing improvements in transport eiciency… ¢ptimisation o production processes with more outsourcing o speciic unctions over time led to a rise in global supply chains… Figure 14 evelopment o global exports relative 0.40 to global € 0.35 Exports to GDP (nominal) 0.30 Exports to GDP (real) 0.25 0.20 0.15 0.10 70 75 80 85 90 95 000 05 10 15 19 19 19 19 19 19 2 20 20 20 Exports to GDP (real)Exports to GDP (nominal) Pre-crisis tren (real) ecessions rey bars indicate global recessions‰ e«uali§ed with global real € growth below 1ˆŸ the dashed line shows the preŽcrisis trends according to the average growth rates between 1¡¡0 and 200ƒ… „ource“ Œorld ¦an‰ „wiss ˜e Economic ˜esearch ™ —onsulting… ‘owever‰ trade has grown in line with There has been a slowdown in global trade in more recent years… This appears more € in more recent years… pronounced in nominal terms than in real terms because“ ̤ ‹„ appreciation“ national values need to be converted to a common currency‰ typically the ‹„… stronger ‹„ reduces the value o exports denominated in other currencies‰ even i prices in local currency terms and volumes increase… The same applies to world €… ‘owever‰ as the ‹„ accounts or a smaller share o world trade than it does or world €‰ converting local currencies to ‹„ to aggregate nominal trade and € causes the ratio between the two variables to decline as the ‹„ appreciates… ̤ ¥alling commodity and manuacturing prices in recent years have led to lower export prices †see ¥igure 1‡… —ommodities and manuactured goods account or a larger share o trade than they do or global output… ecreasing commodity and manuacturing prices thereore have a larger negative eect on nominal exports than on nominal €‰ causing the ratio between the two variables to decline… 9 … rwin‰ “”ongŽrun trends in world trade and income”‰ World Trade Review, 1†1‡ 2002‰ pp… ¡–100… 10 —… —onstantinescu‰ … ‚attoo and ‚… ˜uta‰ “The lobal Trade „lowdownŸ —yclical or „tructural¬”‰ IMF Woring Paers, 1†6‡‰ 201… 16 Swiss Re sigma No 3/2016
 World Insurance in 2015 Page 22 Page 24
World Insurance in 2015 Page 22 Page 24